Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of increasing the volume and quality of traffic to a website through organic search results. It is crucial to your content marketing strategy. SEO experts achieve successful results by developing engaging content, designing technically compliant web pages and leveraging sophisticated software tools to better understand complex search algorithms.
The process of optimization is open-ended. As search providers like Google update their algorithms, consumers change their behaviors and regulatory bodies impose rules on web content, SEO experts must continually evolve their systems and processes.
Learning SEO is a lifelong pursuit in many ways, but you can pick up the basics quickly by turning to experts in the field. We’ve collected 16 of the most common SEO questions and sought out answers from leading SEO professionals:
1. What role does content play in effective SEO?
Content is one of the most important SEO factors because without it, there would be nothing for your readers to engage. When we use the word “content” here, we mean anything from the written word to visual graphics. Some of the most common types of content used for SEO purposes include:
- Written content: Blog articles, landing pages, white papers, eBooks, case studies, etc.
- Visual content: Graphics, infographics, videos, animations, .GIFs, etc.
- Audio content: Podcasts, audiobooks, etc.
Brafton Marketing Specialist Dominick Sorrentino has written extensively about how content satisfies search intent and boosts SEO objectives.
“Google’s algorithms know authentic collateral when they see it, so content for SEO needs to be smart and engaging but also backed up with strong web design and UX,” Dom wrote, alluding to the integrated nature of SEO. Not only does your content need to be high-quality to appeal to your target audience (humans), but also structured well enough to be readable by search crawlers (robots).
2. What is the most important thing to look for when doing keyword research?
According to renowned SEO expert Neil Patel, keyword research is the most important part of digital marketing.
Neil puts it simply: “Keywords determine what your company is known for.”
When you start your digital marketing efforts with keyword research, you set yourself up for success. Keyword research helps you understand what your target audience is searching for and what language they use. This in turn helps you develop quality content that speaks directly to your audience’s most pressing needs.
When you publish content online, you’re competing with hundreds if not thousands of other brands and individuals. Therefore, Neil recommends focusing on long-tail keywords, which are phrases that allude to more specific search intent.
For example, the keyword “coffee” might look good because it has high search volume — but it’s going to be tough to outrank national brands. A long-tail keyword like “best coffee cocktails in Denver” is more specific. So when you’re conducting keyword research, look for long-tail keywords that are more unique to your offerings and your customers’ needs.
3. How quickly after making changes to a page should you expect to see an SEO impact?
When you publish a piece of content, it is instantly available for all the world to see … if they have a direct link. Chances are, you won’t see your shiny new landing page appear on page 1 of a SERP for several weeks to a few months. This is due to several factors, including the sheer size of the internet, your competitors and how trustworthy your content appears to web crawlers.
Veteran SEO professional Jeremy Knauff, writing in Search Engine Journal, explained that companies need to be prepared to invest several months to a year before seeing results from SEO efforts.
“You can’t accurately predict exactly how long SEO takes until you start putting in the work,” Jeremy explained. “However, you can make a highly educated guess based on certain variables, and then, over time, you can get a better idea of how long it may take within your particular niche against your competitors.”
So, for example, a niche company selling into a local market will likely see faster results from their efforts than a retailer wading into a new regional market against heavy competition.
4. What is the difference between page rank and search engine results page?
Like many industries, SEO brings with it a lot of jargon that can be confusing to newcomers. Two phrases you’re likely to encounter include page rank and search engine results page. Let’s start with the latter, because you’re already familiar with it — even if you don’t know it.
A search engine results page (SERP) is what you see when you type a query into Google or your favorite search engine. It’s essentially a list of links, though it has grown more sophisticated over the years. For instance, if you search for “SEO” you’ll not only see a list of links, but also a definition, a collection of frequently asked questions and maybe a few related queries.
A page rank, however, is a numeric value representing how important a page is in the eyes of a search engine algorithm. In fact, back in the ancient days of the internet (read: 1997), Google used a mathematical formula dubbed PageRank to quantify the value of pages on the internet. Until some time in 2016, you could use the PageRank toolbar to actually see the rankings awarded to individual pages. Although the tool is discontinued, Tim Soulo, CMO of SEO company Ahrefs, has explained that the concept of page rank is still relevant. His explanation is a good read for anyone interested in the deep technical work going on behind the scenes of every Google search.
5. How much do broken links impact your optimization efforts?
You likely already know that broken links harm the user experience, and that in itself should be reason enough to fix them. It’s frustrating to arrive at a page that should have the information you need, only to find a tacky 404 message.
But did you also know that broken links can have a detrimental effect on SEO? Remember, it’s not just the human beings in your target audience who are browsing your website, but also Google’s web crawlers. These robots scan your website and follow the links they find. If those links are broken, it signals that the page is not of high quality. This goes for broken links to internal pages as well as links to broken pages on external websites.
Internet Marketing Specialist Kayla Tarantino compared broken links to a heartbreaking Valentine’s Day scenario: “When visitors follow links to or from your site they are expecting certain content to be available to them once they get to that page. Broken links are not only bad for user experience but can also be harmful to your site’s loving relationship with Google, i.e. your SEO.”
6. What are the most important SEO ranking factors?
There are more factors than we can discuss here, but never fear — Brafton’s own Creative Director of Copy and SEO Michael O’Neill has put together a comprehensive local SEO checklist. The search signals he discusses are important for general SEO, as well.
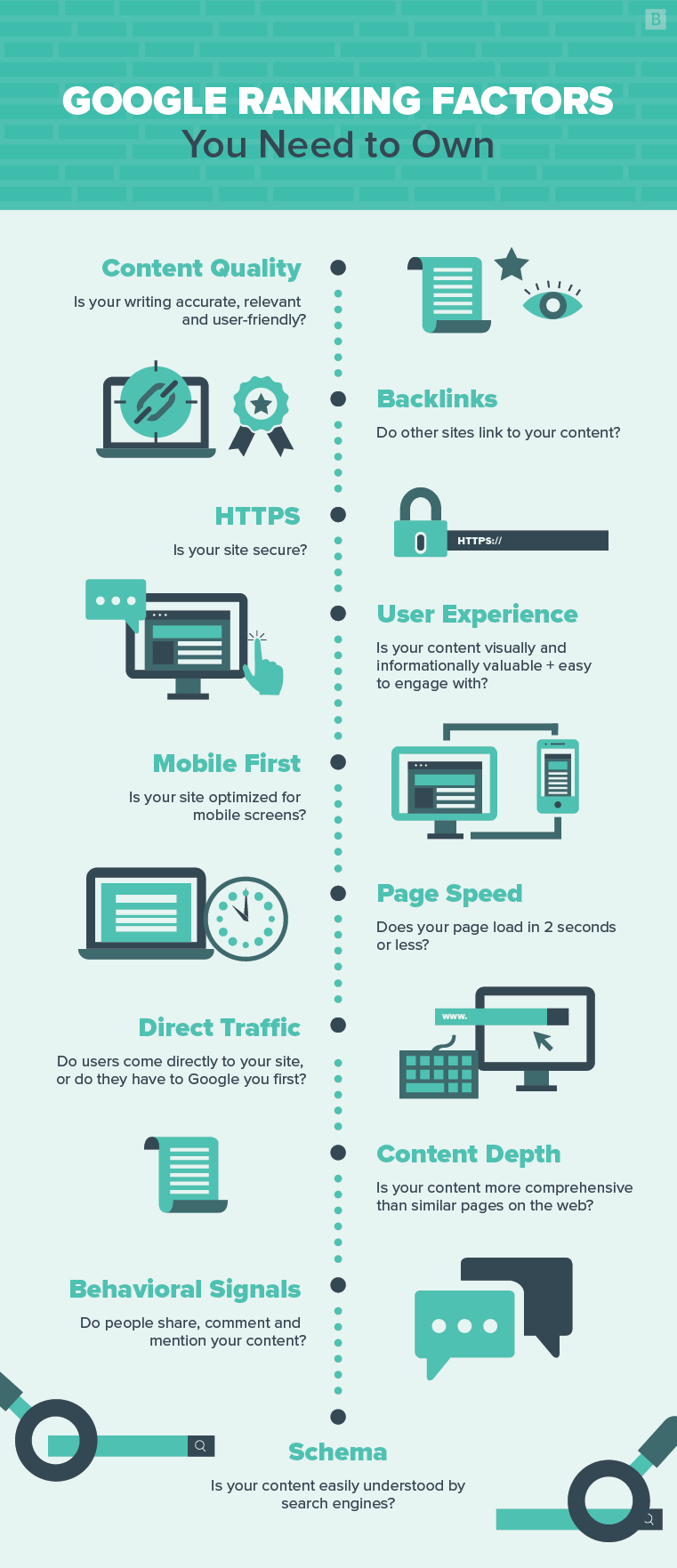
7. What is page speed and how does it affect SEO?
We’ve all been in this situation: You enter a query into Google and click on a link that looks good and the page starts to load. It’s blank, but you can see it loading for one second, then two — and then you click the back button. Who has the time to wait for a third second?
According to the experts at Moz, page speed can be defined in two ways:
- Page load time: The time it takes to fully display the page’s content.
- Time to first byte: How long it takes for your browser to get the first byte of information from the web server.
Page speed is widely considered to be one of the signals Google uses to rank pages in SERPs. We can’t say for certain, because Google has never and will never reveal its secret algorithmic sauce. But considering how important speed is to the user experience, it’s a safe bet Google uses it to quantify the value of a page.
In the scenario described above, leaving the page before it loads indicates a poor user experience. If many users have the same experience, there’s a good chance that Google will lower that page’s ranking, favoring another page that can offer a better experience.
8. What is link building and is it still relevant to SEO?
At its core, the internet is built on a series of connections. The web simply couldn’t exist on a single machine. Web servers and internet service providers across the globe make it possible to seek out and view content across the web.
Link building is an essential part of SEO because it is one way that search algorithms determine a page’s trustworthiness and quality. It is the practice of getting other websites to link back to your own. For instance, many of the hyperlinks in this article will direct you to other websites where experts have written about the subject of SEO. The writer of this article (Hello) considers those sites to be trustworthy and of high quality. If many other people also consider them to be trustworthy, they too will link back to those sites. Google sees this behavior and uses it as a factor when ranking sites in SERPs.
As SEO factors go, link building is one of the most difficult to improve upon, but it can have the highest reward. This is because it can have a snowball effect. For example, we know that Energy.gov is considered a trustworthy site. So, if Energy.gov were to link to your site, some of its trustworthiness would get passed on to you. Plus, the right backlink can drive a ton of traffic to your site.
Brafton writer Nick Kakolowski has written an advanced guide to link building that delves deeper into this complex and important SEO topic.
9. How do you measure and track your SEO efforts?
The O in SEO means you must continuously measure your efforts and make adjustments to your strategy in response to numerous factors. As your competitors publish content, update their websites and build their own link strategies, they may edge you out of the top spot.
While there are many tools available to monitor your SEO efforts, Google Analytics is the industry standard. Not only is it feature-rich and easy to use, but it’s also free. Once you get your GA account set up and connected to your site, you’ll get new data every day, showing you how visitors interact with your content.
The importance of tracking your visitor behaviors cannot be overstated. Your GA data can show you which pieces of content perform the best, helping you optimize and promote them. Likewise, you’ll see which pieces underperform, so you can make informed decisions about how best to troubleshoot them.
Getting started with GA can seem daunting at first, but we’ve got you covered with our answers to GA frequently asked questions.
10. What SEO tools should you use?
GA is far from the only SEO tool the pros use to meet and exceed their optimization goals. In fact, the selection of available tools can be overwhelming. And while you may not need to use a dozen different tools to develop and promote your web content, it’s best practice to use one or two to make sure you’re on the right track.
If you only use one SEO tool — other than GA — it should be a keyword research tool. Without proper research, you could end up wasting your time and energy on content that no one is searching for. At Brafton, we like SEMrush, which features a Keyword Magic Tool that makes research a breeze.
Check out our list of 20 SEO marketing tools to see just how many options are available. You’ll find free and paid versions of various tools to help you optimize your content, develop your strategy and produce engaging content.
11. What is the process for conducting SEO research?
At a basic level, SEO research comes down to finding the right keywords for your brand, targeting those keywords through content and optimizing that content over time. Piece of cake, right? Actually, the process can be rather involved — but don’t let that stop you! SEO can be hard work, but it pays off with more traffic to your website.
To better understand what this process looks like, we turn again to Ahrefs CMO Tim Soulo, who describes the practice of finding the right keywords in four steps:
- Brainstorm seed keywords: Start with a basic keyword that is related to your brand, product or service.
- Monitor your competitors: Find out which keywords your competitors rank for — this is where some of those SEO tools will come in handy.
- Find niche keywords: Using a tool like SEMrush, you can use your seed keywords to uncover related keywords that are easier to rank for, yet still relevant to your goals.
- Study your niche: Research your target audience to understand what they’re searching for online. This will help you create keyword rich content that addresses your customers’ needs.
12. Does SEO work for images and videos?
In general, it is more difficult to optimize images and videos for search engines. This is because web crawlers can’t really read the text in images nor can they actually “see” the images to understand what is being displayed. However, it’s still possible, and important, to optimize your visual content as much as possible.
The easiest way to do so is to couch your visual content within written content. For example, if you’ve created an eye-catching infographic, you can place it within an SEO blog. This way, the web crawlers can read the content and understand what’s on the page.
Another good SEO best practice is to include descriptive alternative text for any images included in your content. This serves two purposes: It helps web crawlers understand the content and it makes it easier for visually impaired members of your audience to browse your content.
For more technical ways to optimize your images, videos and other rich media, check out Google’s advanced SEO guides.
13. What is the difference between on-page and off-page SEO?
To put it simply, on-page SEO is all of the things within your control, and off-page SEO is everything outside of your control. In fact, the term on-page can be a little misleading, because it also refers to things like a page’s meta description, meta tag, title tag, URL structure and other technical SEO items.
SpyFu writer and SEO specialist Sidra Condron explains the two-sided nature of SEO:
“In today’s competitive SEO market, amazing content unfortunately isn’t enough. Ranking well in the SERP isn’t just about finding the right keywords and writing an article. You need to consider the structure of your website and the technology used to create it and how that impacts both readers and search engine crawlers.
Once your website is live, it’s time to think about how to garner high-quality backlinks and get your readers to share your site with their networks. All of this contributes to the overall strength of your domain.”
When it comes to off-page SEO, you do have some influence. For instance, you can create social media posts to encourage others to share your content. Or, you can reach out to other websites to ask them to link to your website. Make sure you put your effort into on-page SEO before doing the hard work of trying to influence others.
14. What is black hat SEO? What is white hat SEO?
These terms refer back to old western movies in which the good guy wears a white hat and the bad guy wears a black hat. As far as industry jargon goes, these terms are almost as old as those black-and-white movies.
Essentially, black hat SEO refers to unsavory practices that attempt to go around the rules to get pages to rank highly. In the old days, black hats would stuff websites with hundreds of hidden keywords — for example, using white text on a white background — to trick algorithms into giving the pages a high rank.
Over the 20+ years of SEO history, search providers like Google have gotten very good at cracking down on bad behavior. It’s harder than ever to game the system, so you’re better off not trying.
SEO consultant Helen Pollitt writes about black hats, white hats and gray hats at Search Engine Journal. Check out her explanation of the terms for more examples of good and bad SEO behaviors.
15. What are rich snippets?
Even if you’re not familiar with the term, you’ve seen rich snippets in action. Type any search term into Google, and you’re likely to find that some results contain more information than others. Rich snippets are a type of structured data that enable Google to provide additional context around links.
For example, if you search for a fudge brownie recipe, you’ll probably see that some recipes feature an image and a star rating. This shows you what other people have thought of the recipe.
Brafton’s Michael O’Neill writes about the various types of rich snippets and why you should care about them.
16. Will SEO ever become obsolete?
It’s easy to see why some people think SEO is dead or dying or about to die. After all, the SEO of today looks nothing like the SEO of 1999. The fact is that the practice of SEO is always evolving. While today’s SEO might become obsolete, there will always be a need for SEO as long as search engines exist.
With the right SEO strategy, you can begin to see substantial results in just a few months. Check out our recent case study to learn how we went from zero to revenue in just 9 months in the Australian market.